Blender GIS is a powerful open-source software that seamlessly combines the capabilities of Blender, a renowned 3D modeling and animation tool, with the functionalities of a Geographic Information System (GIS). With Blender GIS, users can effortlessly import, visualize, and analyze spatial data within a 3D environment, unlocking a world of possibilities for creating stunningly realistic maps, models, and simulations. This open-source add-on for Blender empowers users to import and manipulate geographic information system (GIS) data, enabling the creation of immersive 3D models that accurately represent real-world landscapes, buildings, and various other objects. Whether you’re an aspiring 3D artist, GIS professional, or someone passionate about exploring the potential of GIS data, Blender GIS offers an exceptional toolset for creating captivating and interactive 3D visualizations.
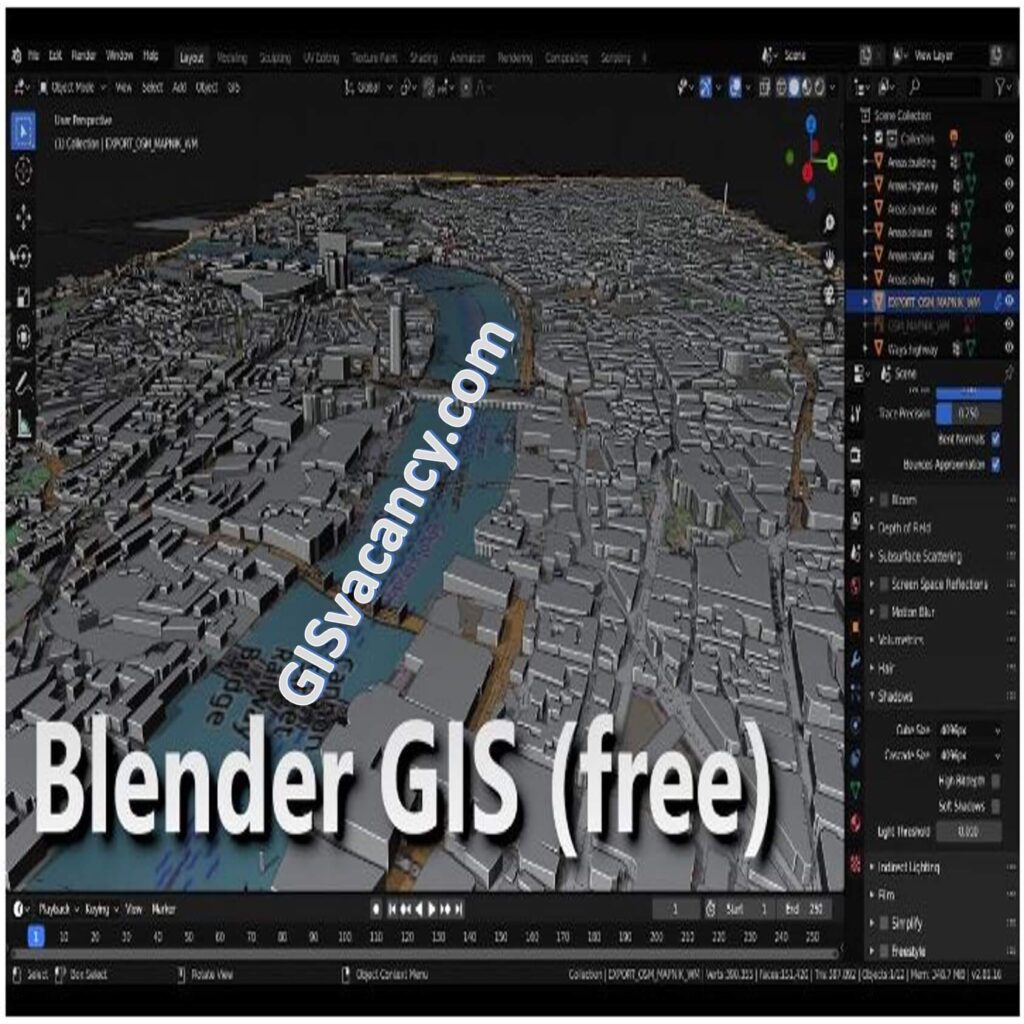
Some of the features of BlenderGIS include:
- Importing GIS data in a variety of formats, including Shapefiles, GeoTIFFs, and OpenStreetMap XML
- Creating 3D models of terrain, buildings, and other objects
- Adding textures and materials to 3D models
- Animating 3D models
- Exporting 3D models to a variety of formats, including OBJ, FBX, and STL
BlenderGIS is a free and open-source software, so it is available to anyone to use. It is a powerful tool for anyone who wants to create realistic and interactive 3D visualizations of GIS data.
Some examples of what you can do with BlenderGIS:
- Create a 3D model of your city
- Create a 3D model of your neighborhood
- Create a 3D model of your school
- Create a 3D model of your favorite park
- Create a 3D model of your favorite landmark
- Create a 3D model of your favorite vacation spot
- Create a 3D model of your dream home
Importing GIS Data into Blender
To import GIS data into Blender GIS, follow these steps:
- Install the Blender GIS add-on: Download and install the Blender GIS add-on, which extends Blender’s functionality with GIS tools.
- Prepare your GIS data: Ensure your GIS data is in a compatible format, such as shapefile or geodatabase. If needed, convert the data to the appropriate format using GIS software.
- Open Blender and enable the Blender GIS add-on: Launch Blender and navigate to the add-ons section in the preferences. Enable the Blender GIS add-on.
- Import the GIS data: In Blender, go to the File menu and select “Import.” Choose the appropriate GIS data format and locate the file you want to import. Follow the prompts to import the data into Blender.
- Adjust data properties: Once imported, you can adjust properties and attributes of the GIS data within Blender GIS to fit your needs. This includes modifying scale, rotation, materials, and textures.
Spatial Data Visualization in Blender GIS
Blender GIS provides various tools and techniques for spatial data visualization. Here’s how to make the most of them:
- Apply materials and textures: Enhance the visual appearance of your imported GIS data by applying materials and textures. This can include assigning realistic textures to terrain, buildings, or other objects in your 3D scene.
- Utilize lighting techniques: Experiment with different lighting setups to create the desired ambiance in your 3D maps. Adjust the position, intensity, and color of lights to highlight specific features or create realistic day and night scenes.
- Employ camera settings: Set up camera angles and perspectives to capture the best views of your spatial data. Adjust the camera position, rotation, field of view, and depth of field to create compelling visual compositions.
- Leverage animation features: Take advantage of Blender’s animation capabilities to create dynamic visualizations. Use keyframes to animate camera movements, object interactions, or time-based changes in your spatial data.
Spatial Data Analysis with Blender GIS
Blender GIS offers capabilities for spatial data analysis. Here are some ways to utilize them:
- Measure distances, areas, and volumes: Use Blender GIS’s measurement tools to calculate distances between points, areas of polygons, or volumes of 3D objects. This can be useful for conducting spatial analysis or obtaining quantitative measurements from your 3D models.
- Perform geospatial queries: Blender GIS enables you to query spatial data based on specific criteria. You can select objects within a defined area, filter data based on attribute values, or perform spatial overlays to analyze relationships between different GIS layers.
- Visualize data attributes: Utilize Blender’s visualization capabilities to create thematic maps based on attribute data. Apply color gradients, symbology, or labels to represent different values or categories, allowing for data-driven visualizations and analysis.
Blender GIS Add-ons and Plugins
Blender GIS can be extended with various add-ons and plugins to enhance its functionality. Here are some recommended ones:
- GIS Blender Tools: This add-on provides additional tools for spatial data analysis, including geoprocessing operations, network analysis, and spatial statistics. It expands the capabilities of Blender GIS and allows for more advanced spatial analysis workflows.
- OSMImporter: With this plugin, you can import OpenStreetMap (OSM) data directly into Blender GIS. It enables you to bring in detailed road networks, buildings, and other OSM features to create realistic urban environments and landscapes.
- QGIS Blender: This plugin enables seamless integration between Blender and QGIS, a popular open-source GIS software. It allows you to exchange data between the two platforms, making it easier to leverage the strengths of both Blender GIS and QGIS in your GIS projects.
- BlenderGIS for Unity: This plugin facilitates the transfer of GIS data from Blender GIS to Unity, a real-time development platform. It enables you to create interactive 3D applications, simulations, or games using GIS data generated in Blender.
- Landscape Generator: This add-on provides tools for generating realistic landscapes and terrains within Blender GIS. It allows you to create mountains, valleys, rivers, and other natural features, making it ideal for environmental simulations or visualizations.
Conclusion
Blender GIS is a powerful tool that brings together the worlds of GIS and 3D mapping. With its capabilities for importing GIS data, visualizing spatial information, conducting spatial analysis, and the availability of add-ons and plugins, Blender GIS offers endless possibilities for creating stunning maps, models, and simulations. Whether you’re a GIS professional, a 3D artist, or a spatial data enthusiast, Blender GIS can revolutionize the way you work with spatial data. Explore its features, experiment with different techniques, and unlock the potential of 3D mapping and visualization in your GIS workflows.
We hope this blog post has provided you with a comprehensive overview of Blender GIS and its various functionalities. Start exploring the world of 3D mapping and visualization with Blender GIS today!

